
Stable and powerful ion batteries are required by all of us as they power everything from cellphones, electric cars, electric bikes, electric scooters, hoverboards, flying drones, and various other appliances etc.
New Organic Material
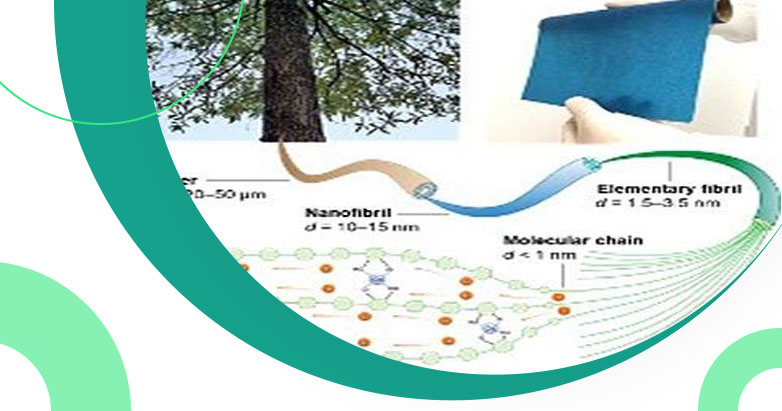
Scientists and researchers from Brown University and the University of Maryland are working on creating new battery material to be utilized instead of using current ion conduction liquids used in today's solid-state batteries. The new material is derived from trees.
Better Conductivity
The research team demonstrated that the new material is paper-thin and highly conductive having 10 to 100 times better in comparison to other polymer ionic materials and conductors. The new material can be used for solid-state batteries as an electrolyte or as an ionic binder.
Professor Liangbing Hu (University of Maryland) states that “Using copper as cellulose nanofibrils, the research team was able to provide better lithium-ion transport within the polymer chains”. The research work is a collaboration between Yue Qi’s lab of Brown University and Hu’s lab at the University of Maryland.
Lithium-ion batteries generally have had lithium salt based electrolytes in the form of liquid solvents. Electrolytes primary purpose is to conduct electricity by passing lithium ions from the cathode and anode side of the battery.
Drawback of Liquid Electrolytes
Liquid conductors or electrolytes have worked well but have a few drawbacks. Electrolytes can short circuit due to the creation of dendrites having small lithium metal filaments occurring due to high currents towards the battery. Liquid conducting materials are highly toxic and flammable which can catch fire easily.
Solid electrolytes are made from non-flammable material and therefore can prevent dendrites. Ceramic materials have been found to have excellent conductivity as solid electrolytes but are brittle, thick and hard. Ceramics as solid electrolytes are unstable as stress or charging can lead to breakage and cracks.
Benefits of New Organic Material
The new material from wood is flexible and thin like a piece of paper having excellent ionic conductivity that is matching to ceramics. Researchers at the Brown University Qsheng Wu and Qi showcased computer simulations illustration of microstructure towards copper or cellulosic material to understand ion conductivity.
Various studies have showcased that copper is responsible for creating tight packed bundles by increasing space towards cellulose polymer chains generating higher ion conductivity towards lithium batteries.
Dr. Qi states that having lithium ions better conductivity and travel within newly found organic electrolyte material through processes previously applied towards inorganic ceramics generating great iconic conductivity. The new organic material will greatly impact the better environment by lowering the impact of harmful chemicals from current batteries.
Cathode Binder Function
The new organic material can also function as a cathode binder for all solid batteries. Cathode needs thickness to work along the anode however it can also reduce efficiency. Working for cathodes requires that they be ionic conductive binder wrapped. The research team illustrated the usage of the new organic material as binder as it becomes the thickest working cathodes that are reported to be working.
According to a recent study in 2020, the lithium-ion market globally was $ 40.5 billion in 2020 which is expected to reach $92 billion in the year 2026.
Researchers believe and hope that the new organic material will be a new step towards bridging the gap towards providing solid-state battery technology towards the market.










.gif)


































