-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
This online test contains MCQs about following topics:
Introduction to random variables . Random numbers and their generation . Application of random number . Concept of random variable and their construction from different fields . Discreate and continuous random variables
MCQ's Test For Chapter 7 "Statistics Ics Part 1 Chapter 7 Online Test"
Try The MCQ's Test For Chapter 7 "Statistics Ics Part 1 Chapter 7 Online Test"
-
Total Questions17
-
Time Allowed20
Question # 1
probability distribution of a continuous random variable can be presented by.
Question # 2
If two coins are tossed, the probability of getting one head and one tail is.
Question # 3
E(y-μ) is equal to
Question # 4
Var (B/aX) =?
Question # 5
The probability of getting one red ball from a bag constaining 4 red, 3 white and 3 black balls is.
Question # 6
The simplest form of the continuous distribution is the.
Question # 7
For a constant K ,the variance of K.
Question # 8
If one event is unaffected by the outcome of another event, the two events are said to be
Question # 9
Tossing two dice possble sampes are.
Question # 10
The probability of red card out of 52 cards is.
Question # 11
Why are the outcomes of a coin tossing mutually exclusive.
Question # 12
Which is the impossible event when a dice is rolled.
Question # 13
F(y1) ≤ F(y2) if
Question # 14
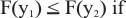
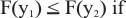
Question # 15
The probability distribution of discrete random variable is called is
Question # 16
If x and y are independent random variables, then E(xy)
Question # 17
The probability of continuous random variable at x = a is__________.
ICS Part 1 Statistics Chapter 7 MCQs Test
Top Scorers Of Chapter 7 "Statistics Ics Part 1 Chapter 7 Online Test" MCQ`s Test
-
E Eman Asif 09 - Aug - 2021 01 Min 26 Sec 17/17 -
W Waseem 13 - May - 2022 02 Min 24 Sec 17/17 -
Z zakria asif 03 - Jun - 2021 03 Min 23 Sec 17/17 -
N Noor Fatima 3207 30 - May - 2022 07 Min 52 Sec 17/17 -
@ @immortal.Sameer 09 - Aug - 2021 01 Min 21 Sec 16/17 -
S shais 12 - Aug - 2021 01 Min 27 Sec 16/17 -
A Adnan Bashir 09 - Jan - 2022 03 Min 37 Sec 15/17 -
R Rameen Basit 08 - Jun - 2023 04 Min 50 Sec 15/17 -
Z Zakria Awan 11 - Dec - 2021 06 Min 11 Sec 15/17 -
E EDITS x FANPAGES 30 - Jun - 2022 04 Min 33 Sec 14/17 -
R Raheema Fayyaz 17 - Apr - 2024 14 Min 28 Sec 13/17 -
A Ayesha Razzaq 13 - Jan - 2022 05 Min 08 Sec 12/17 -
Z Zuhaib Nadeem 12 - May - 2023 10 Min 13 Sec 12/17 -
W Waqas Nisar 15 - Mar - 2024 06 Min 07 Sec 11/17 -
I Iram Salem 11 - Jan - 2022 08 Min 27 Sec 11/17
ICS Part 1 Statistics Chapter 7 Important MCQ's
| Sr.# | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | If x and y are independent random variables, then E(xy) |
A. E(xy)
B. xE(y)
C. E(x)
D. E(x)E(y)
|
| 2 | Why are the outcomes of a coin tossing mutually exclusive. |
A. The outcome of any toss is not affected by teh outcome of those preceding it.
B. Both a head and a tail cannot turn up on any one toss
C. The probability of getting a head and the probability of getting a tail is the same.
D. All of these
|
| 3 | A random variable is also called. |
A. Chance variable
B. Stochastic variable
C. Discrete variable
D. Both A and B
|
| 4 | Hourly temperature recorded by weather brave is the example of: |
A. Discrete variable
B. Continuous variable
C. Qualitative
D. Both A and B
|
| 5 | Which one is not an example of random experiments. |
A. A coin is tossed and the outcome is either a head or a tail
B. A six sided aid is rolled
C. All medical insurance clams received by a company in a given year.
D. Some one of person will be admitted to a hospital emergency room during any hour.
|
| 6 | If a is a constant then E(a) is equal to |
A. a
B. Square of a
C. Zero
D. 2a
|
| 7 | E(x) = Σxf(x) if it ________ absolutely. |
A. Equal
B. Converges
C. Discrete
D. None of these
|
| 8 | The probability of getting one red ball from a bag constaining 4 red, 3 white and 3 black balls is. |
A. 3/10
B. 1/5
C. 2/5
D. 1/2
|
| 9 | Tossing two dice possble sampes are. |
A. 2
B. 6
C. 12
D. 36
|
| 10 | The range of probability is between |
A. 0 to 2
B. -1 to +1
C. 0 to 8
D. 0 to 1
|








.jpg)












Share your comments & questions here
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!