-
 Home
Home
-
 News
News
Latest Educational News Stories
Daily update of all national, international news, picture stories, college / university announcements and educational events.
-
 Colleges
Colleges
Pakistan's Largest Database of Colleges and Universities
Explore Largest Directory of Private and Govt. Colleges, Universities and find best institute for your future Education.
-
 Courses
Courses
-
 Admission
Admission
-
 Lectures
Lectures
-
 Online Test
Online Test
Short Question
- 9th Class Physics Short Questions
- 9th Class Chemistry Short Questions
- 9th Class Math Short Questions
- 9th Class Biology Short Questions
- 9th Class Computer Short Questions
- 9th Class English Short Questions
- 10th Class Physics Short Question
- 10th Class Chemistry Short Question
- 10th Class Math Short Question
- 10th Class Biology Short Question
- 10th Class Computer Short Question
- 10th Class English Short Question
-
 Past Papers
Past Papers
-
 Date Sheets
Date Sheets
-
 Results
Results
Exam Results 2024
Check online Results 2024 Matric Inter BA BSc B.Com MA MSc M.Com CSS PCS MCAT ECAT of all educational boards and universities in Pakistan
-
 Study Abroad
Study Abroad
Study Abroad Programs and Opportunities for Pakistani Students
Explore free study abroad search to find programs, consultants, events to study in USA, UK, Australia, China, Malaysia and many others.
-
 Jobs
Jobs
-
 Tutors
Tutors
-
 More
More
-
 Apps
Apps
MCQ's Test For ECAT Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical Equilibrium
Try The MCQ's Test For ECAT Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical Equilibrium
-
Total Questions30
-
Time Allowed30
Question # 1
What happens when reaction is at equilibrium and more reactant is added :
Question # 2
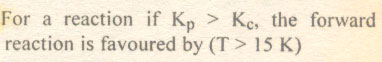
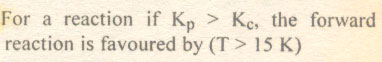
Question # 3
The rate of a chemical reaction is directly;y proportional to product of molar concentration of reaction substance it is called :
Question # 4


Question # 5
If pH of buffer of 1 mole dm-3of HCOOH + 0.1 mole dm-3HCOONa having pKa = 3.78 is
Question # 6
Which of the following is a characteristic of a reversible reaction?
Question # 7
The relation between Kc and Kp is
Question # 8
1 mol of N2O4 was decomposed according
to given equation in 1dm3 container. At equilibrium x mole of N2O4
have dissociated. What is the value of KC:
Question # 9
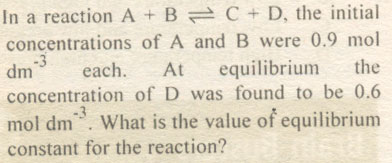
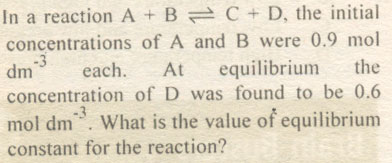
Question # 10


Question # 11
A chemical reaction is in equilibrium when
Question # 12
Addition of solid NaHCO3in water causes ionization of NaCHO3its Ka= 4.7 x 10-1. Then this solution has character
Question # 13
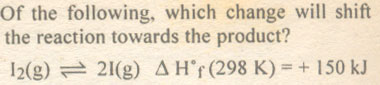
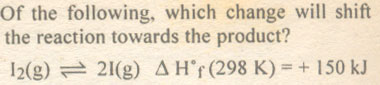
Question # 14
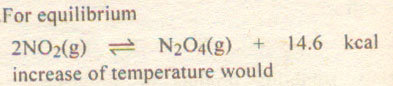
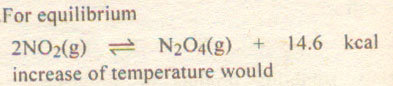
Question # 15
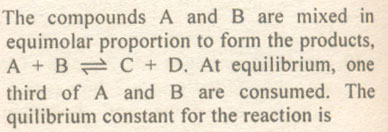
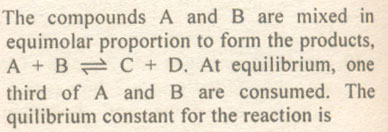
Question # 16
For what value ofKc almost forward reaction is complete :
Question # 17
Law of mass action was given by :
Question # 18
I a chemical reaction equilibrium is said to have been established when :
Question # 19
0.1 MHCI has pH = 1.0, it is about 100 times stronger than acetic acid. Then pH of acetic acid will be
Question # 20


Question # 21
A solution has pH = 0, its H+ion concentration is
Question # 22
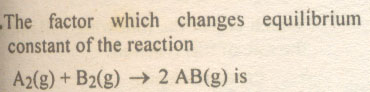
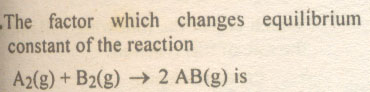
Question # 23
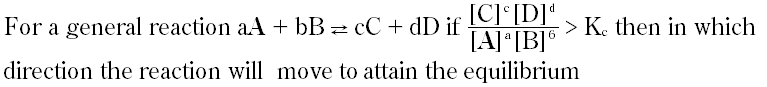
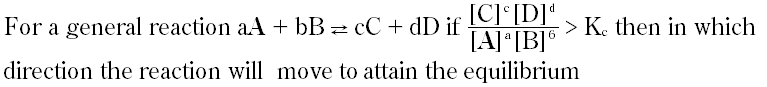
Question # 24
Reactions that proceed on both sides and never go to completion are called
Question # 25
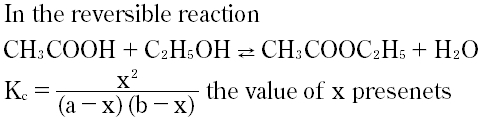
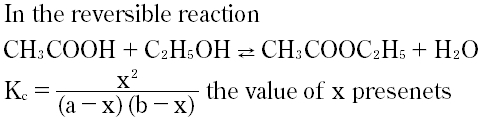
Question # 26
The solubility product of AgCl is 2.0 x 10-10mol2dm-6The maximum concentration of Ag+ions in the solution is
Question # 27
The rate of which the reaction proceeds is directly proportional to the product of the active masses of the reactants is according to
Question # 28


Question # 29
N2 +3H2⇌
2NH3 + Heat for above equation, the
Question # 30
Chemical equilibrium involving reactants and products in more than one phase is called
Top Scorers Of ECAT Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical Equilibrium MCQ`s Test
-
A Arian Ahmed 06 - Mar - 2024 00 Min 04 Sec 115/120 -
H Huzaifa Asim 28 - May - 2024 01 Min 12 Sec 115/120 -
M Muneeb Aslam 03 - Jun - 2024 09 Min 57 Sec 105/120 -
? ?GøÐ øf ?ë??h? 29 - May - 2024 32 Min 31 Sec 95/120 -
H Hamza Malhi 10 - Mar - 2024 14 Min 42 Sec 85/120 -
M Maryam Fatima 19 - Mar - 2024 09 Min 42 Sec 80/120 -
A Ayesha Ch 02 - Mar - 2024 05 Min 34 Sec 75/120 -
F Fatima Tabassum 16 - Jan - 2025 09 Min 48 Sec 65/120 -
E Essa raza 22 - Jun - 2024 09 Min 07 Sec 55/120 -
K kayani 21 - Jul - 2024 09 Min 41 Sec 55/120 -
T Tamshi Sohail 20 - Apr - 2024 23 Min 19 Sec 55/120 -
R random 11 - May - 2024 06 Min 15 Sec 50/120 -
H Haniya Ali 14 - Mar - 2024 14 Min 41 Sec 50/120 -
E Ezzah Ansari 15 - May - 2024 15 Min 25 Sec 50/120 -
M Meena 19 - Apr - 2024 10 Min 19 Sec 45/120
| Sr.# | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The pH of 10-3mole dm-3of an aqueous solution of H2SO4is |
A. 3.0
B. 2.7
C. 2.0
D. 1.5
|
| 2 | ph of the buffer CH3COOh + CH3COONa is 3.76. If the mixture contains 1 molar acetic acid and 0.1 molar sodium acetate, then pKa of this buffer is |
A. 3.76
B. 4.76
C. 5.76
D. 6.76
|
| 3 |
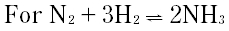
|
A. KC = KP
B. Kp = KcRT
C. Kp = kc(RT)-2
D. Kp = Kc(RT)-1
|
| 4 | Two moles of HI was heated in a sealed tube at 440°C till the equilibrium was reached. HI was found to be 22% decomposed. The equilibrium constant for dissociation is |
A. 0.282
B. 0.0796
C. 0.0199
D. 1.99
|
| 5 | For which system does the equilibrium constant, kc has units of (concentration) ? |
A.
N2+3H2-------2NH3
B.
H2+L2---------2HL
C.
2NO2----------N2O4
D.
2HF--------H2+F2 |
| 6 |
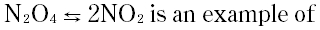
|
A. Reversible reaction
B. Irreversible reaction
C. Spontaneous reaction
D. None of these
|
| 7 | I a chemical reaction equilibrium is said to have been established when : |
A. Rate of opposing reactions are equal.
B. Rate constants of opposing reactions are equal.
C. Opposing reactions stop.
D. Concentration of reactants and products are equal
|
| 8 | If the difference of pKa values of the two acids is 2, then |
A. Acid with smaller pKa is 10 times stronger acid
B. Acid with greater pKa is 10 times stronger acid
C. Acid with smaller pKa is 100 times stronger acid
D. Acid with greater pKa is 100 times stronger acid
|
| 9 | The value of Kpis greater than Kcfor a gaseous reaction when |
A. Number of molecules of products is greater than the reactants
B. Number of molecules of reactants is greater than those of products
C. Number of molecules of reactants and products equal
D. Catalyst is added
|
| 10 |

|
A. 0.12
B. 0.50
C. 0.25
D. 4.00
|
| 11 |

|
A. Le-chatlier's principle
B. Only adding catalyst
C. Decreasing pressure
D. Decreasing temperature
|
| 12 | 0.1 MHCI has pH = 1.0, it is about 100 times stronger than acetic acid. Then pH of acetic acid will be |
A. 0.1
B. 2.0
C. 1.3
D. 3.0
|
| 13 | Buffers having pH less than 7 are made |
A. Mixture of weak acid + salt of it with strong base
B. Mixture of weak acid + salt of it with weak base
C. Mixture of weak base + salt of it with strong acid
D. Mixture of weak base + salt of it with weak base
|
| 14 |
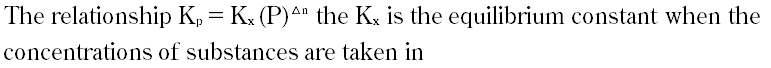
|
A. Moles per dm3
B. Partial pressures
C. Number of moles
D. Mole fractions
|
| 15 | In a reversible chemical reaction having two reactants in equilibrium, if the concentration of the reactants are doubled then the equilibrium constant will |
A. Also be doubled
B. Be halved
C. Becomes one fourth
D. Remains the same
|
| 16 |
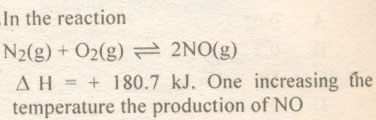
|
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains same
D. Cannot be predicted
|
| 17 | The rate of reaction : |
A. Remain same as reaction proceeds.
B. May decrease or increase as reaction proceeds .
C. Increase as reaction proceeds.
D. Decreases as reaction proceeds.
|
| 18 |
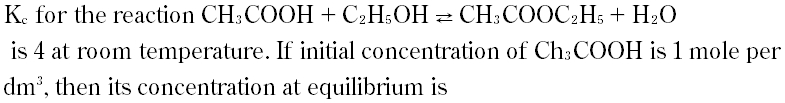
|
A. 4 mole per dm3
B. 2 mole per dm3
C. 0.33 mole per dm3
D. 0.67 mole per dm3
|
| 19 |
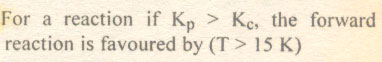
|
A. High temperature
B. Low temperature
C. Low pressure
D. High pressure
|
| 20 |

|
A. The value of Kpfalls with rise in temperature
B. The value of Kpfalls with increasing pressure
C. Addition of V2O5catalyst increase the concentration of SO3
D. The value of Kpis equal to Kc
|
| 21 | If pH of buffer of 1 mole dm-3of HCOOH + 0.1 mole dm-3HCOONa having pKa = 3.78 is |
A. 1.78
B. 2.78
C. 3.78
D. 4.78
|
| 22 | What happens when reaction is at equilibrium and more reactant is added : |
A. Forward reaction rate is increased.
B. Forward reaction rate is decreased.
C. Backward reaction rate is increased.
D. Equilibrium remains unchanged.
|
| 23 |

|
A. High temperature and low pressure
B. Low temperature and low pressure
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
|
| 24 | A buffer solution of 0.1 molar HCOOH and 0.1 molar HCCONa has pH = 3.78 To is 0.01 molar HCl is added, then pH of the buffer solution becomes |
A. 2.78
B. 4.78
C. 3.78
D. 3.70
|
| 25 |
N23H2⇌ 2NH3 Which of the following change will favorthe formation of moreNH3at equilibrium in above reaction : |
A. By adding NH3.
B. By removingH2.
C. By decreasing pressure.
D. By increasing pressure.
|
| 26 |
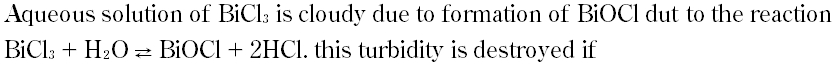
|
A. Temperature is increased
B. Pressure is increased
C. HCl is added
D. HCl is removed
|
| 27 |
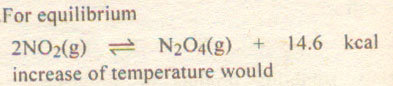
|
A. Favour the formation of N2O4
B. Favour the decomposition of N2O4
C. Not alter the equilibrium
D. Stop the reaction
|
| 28 |

|
A. 0.073
B. 0.147
C. 0.05
D. 0.026
|
| 29 | 1 mole of N2and 2 moles of H2are allowed to react in a 1 dm3vessel. At equilibrium 0.8 mole of NH3is formed. The concentration of H2in the vessel is |
A. 0.6 mole
B. 0.8 mole
C. 0.2 mole
D. 0.4 mole
|
| 30 |
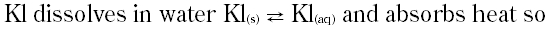
|
A. Decrease in temperature favour more dissolution of the salt
B. Increase in temperature favour more dissolution of the salt
C. Lowering pressure favour more dissolution of the salt
D. Increasing pressure favour more dissolution of the salt
|













