The (OIC) Organisation of Islamic Cooperation is one of the largest international organizations in the world, comprising 57 member states. It was established to promote unity and cooperation among Muslim-majority countries. This article will explore the history, goals, and key achievements of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), its membership, and its role in global politics.
What is the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)?
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote economic, political, and cultural cooperation among Islamic countries. Founded in 1969, the OIC aims to safeguard the interests of the Muslim world and promote peace, security, and development among its member states.
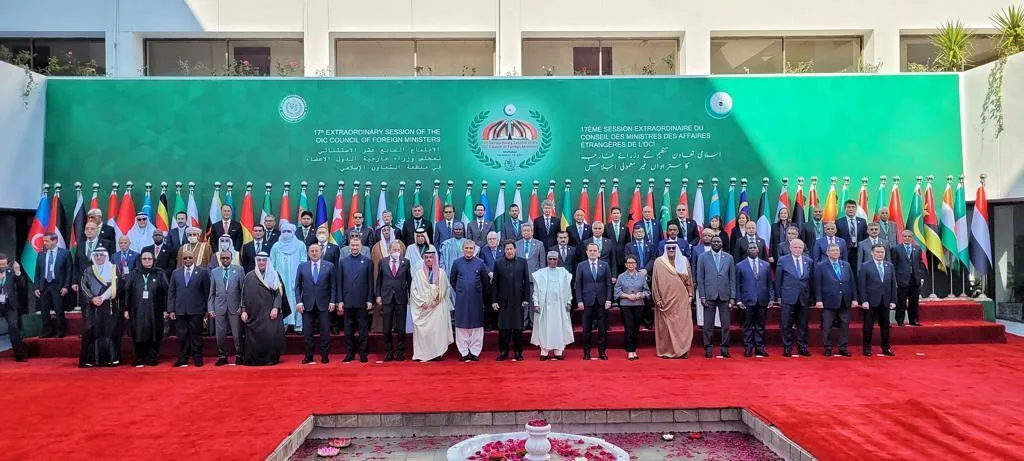

History of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation was established in response to the burning of the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem in 1969. The incident galvanized Muslim-majority countries to create a platform for collective action on issues affecting the Muslim world. The OIC was founded in Rabat, Morocco, with the signing of the Rabat Declaration on September 25, 1969.
The initial goal of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation was to address issues related to the protection of Islamic holy sites, but over time, its focus expanded to include broader political, economic, and social issues affecting member states.
OIC Membership
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation membership includes 57 countries from various regions of the world, including Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. These countries represent a diverse range of cultures, languages, and political systems, but they are united by their shared commitment to the principles of Islam and the values of the OIC.
Member of organization of Islamic cooperation countries
|
Region |
Country |
|
Middle East |
Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Jordan |
|
Africa |
Egypt, Nigeria, Algeria, Morocco, Senegal |
|
Asia |
Turkey, Pakistan, Indonesia, Malaysia |
|
Central Asia |
Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan |
|
Other Regions |
Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Sudan, Somalia |
Goals of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation has several key objectives, which are reflected in its charter. The organization strives to achieve unity and cooperation among Islamic countries while addressing challenges faced by its members. Here are the main goals of the OIC:
1. Promote Unity Among Member States
The OIC aims to promote unity and solidarity among Islamic countries by fostering cooperation in political, economic, and social spheres. This unity is essential for addressing the common challenges faced by member states.
2. Support the Palestinian Cause
One of the central objectives of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation is to support the Palestinian people in their struggle for self-determination and the establishment of an independent state. The OIC has consistently advocated for the rights of Palestinians on the international stage.
3. Defend the Rights of Muslims Worldwide
The OIC works to protect the rights of Muslims in non-Muslim countries and ensure their well-being. The organization addresses issues related to discrimination, human rights violations, and the protection of Islamic culture and heritage.
4. Promote Economic Cooperation
The OIC seeks to enhance economic cooperation among its member states by promoting trade, investment, and development. This includes establishing a common market, facilitating economic partnerships, and addressing issues related to poverty and unemployment.
5. Address Political and Security Challenges
The OIC plays a role in addressing political and security challenges faced by its member states. The organization works to resolve conflicts, promote peace, and foster stability in regions affected by war and unrest.
Organization of Islamic Cooperation Meetings
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation meeting is held regularly to discuss key issues affecting the Muslim world. These meetings provide a platform for member states to coordinate their efforts and adopt resolutions on various political, economic, and social matters.
1. Summit Meetings
The OIC Summit is the highest decision-making body of the organization. It is held every three years and brings together the heads of state or government of all member countries. The summit addresses major issues facing the Muslim world, including conflicts, economic development, and human rights.
2. Ministerial Meetings
In addition to summit meetings, the OIC holds ministerial meetings where foreign ministers of member states come together to discuss specific issues and adopt resolutions. These meetings are held more frequently and serve as a platform for diplomatic engagement.
3. Special Sessions
The OIC also holds special sessions to address urgent matters, such as humanitarian crises, conflicts, or natural disasters. These sessions allow the organization to take immediate action and coordinate assistance to affected member states.
Table: Types of OIC Meetings
|
Meeting Type |
Frequency |
Purpose |
|
Summit Meeting |
Every 3 years |
High-level discussions on key issues |
|
Ministerial Meeting |
Annual or as-needed |
Discussions among foreign ministers |
|
Special Session |
As required |
Urgent discussions on crises or emergencies |
Key Achievements of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation has achieved several notable successes since its establishment. These achievements reflect the organization's commitment to promoting peace, unity, and development among Islamic countries.
1. Advocacy for Palestinian Rights
The OIC has been at the forefront of advocating for Palestinian rights and the establishment of an independent Palestinian state. The organization has consistently called for international recognition of Palestinian sovereignty and has supported Palestine in various international forums.
2. Humanitarian Assistance
The OIC has played a key role in providing humanitarian assistance to member states affected by conflicts, natural disasters, and economic crises. The organization has coordinated relief efforts and mobilized resources to support displaced populations and those in need.
3. Economic Development Initiatives
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation has launched various initiatives to promote economic development among its member states. These initiatives focus on trade, investment, infrastructure development, and poverty reduction. The OIC has also established institutions like the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) to support economic growth in member countries.
4. Conflict Resolution and Peacekeeping
The OIC has been involved in peacekeeping efforts and conflict resolution in several regions, including Sudan, Somalia, and Afghanistan. The organization has worked to mediate peace talks, provide diplomatic support, and promote stability in conflict zones.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)?
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is an intergovernmental organization consisting of 57 member states. It aims to promote political, economic, and cultural cooperation among Muslim-majority countries.
2. How many countries are members of the OIC?
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation membership includes 57 countries, representing a diverse range of cultures and political systems, united by their commitment to the principles of Islam.
3. What is the main goal of the OIC?
The primary goal of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation is to promote unity and solidarity among its member states while addressing political, economic, and social challenges.
4. How often does the OIC hold meetings?
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation meetings are held regularly, with summit meetings occurring every three years, ministerial meetings held annually or as needed, and special sessions convened in response to urgent issues.
5. What are some key achievements of the OIC?
Some key achievements of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation include advocacy for Palestinian rights, providing humanitarian assistance, promoting economic development, and facilitating conflict resolution and peacekeeping efforts.




.gif)















Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com