The term "Roof of the World" is famously attributed to the Tibetan Plateau, the world’s highest and largest plateau. Its unmatched altitude, averaging 4,500 meters (14,800 feet) above sea level, makes it a natural wonder. However, this title is also associated with other high-altitude regions, including the Shandur Pass in Pakistan and the Pamir Mountains in Central Asia. These regions, rich in history and geography, are celebrated for their unique landscapes, cultural significance, and ecological importance.
This article explores the Tibetan Plateau, Shandur Pass, and the Pamir Mountains, delving into why they are called the "Roof of the World", their geographical and cultural significance, and their impact on the world.
The Tibetan Plateau: The True “Roof of the World”
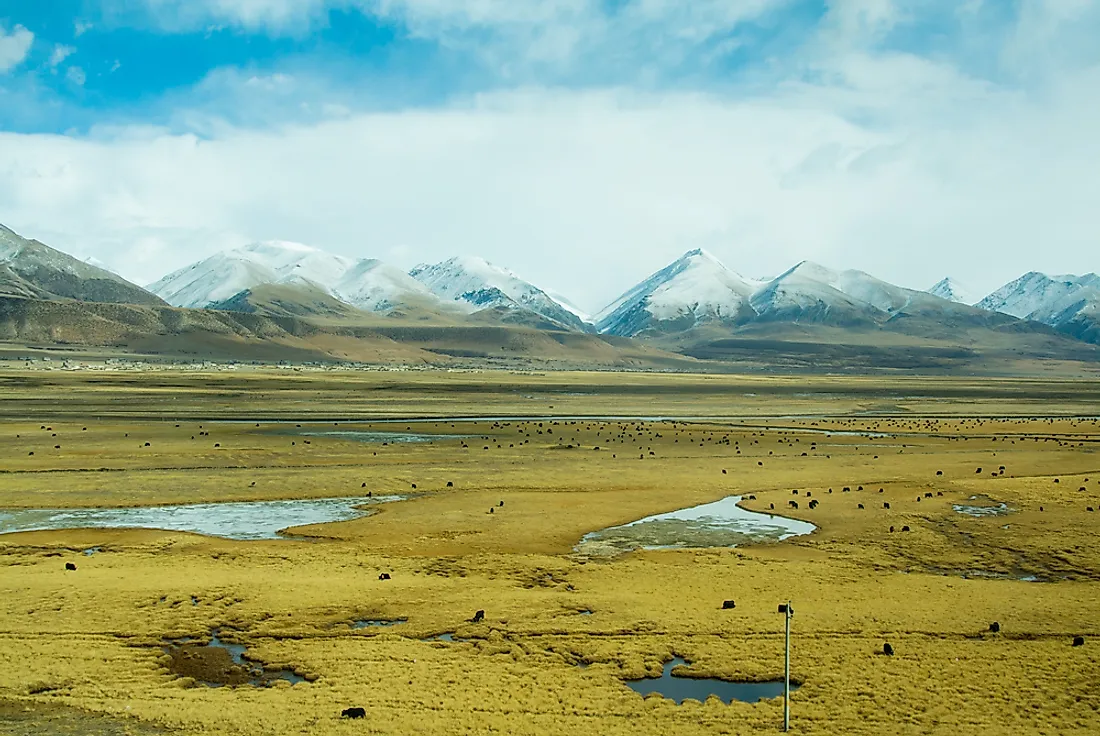
The Tibetan Plateau is the largest and highest plateau globally, often called the "Roof of the World" for its extreme elevation and expansive area of approximately 2.5 million square kilometers. Located in Central Asia, it spans multiple countries, including China, India, and Nepal. This region is surrounded by towering mountain ranges, including the Himalayas and the Kunlun Mountains, making it a geographical marvel.

Key Features of the Tibetan Plateau
-
Altitude and Size
-
Average elevation: 4,500 meters (14,800 feet) above sea level.
-
Covers an area larger than Western Europe.
-
-
Climate and Ecology
-
Known as the "Third Pole", the plateau holds massive ice reserves, second only to the polar regions.
-
It is home to unique flora and fauna, including the snow leopard and Tibetan antelope.
-
-
Cultural Significance
-
The plateau is a spiritual hub, central to Tibetan Buddhism.
-
It hosts many monasteries, including the iconic Potala Palace in Lhasa.
-
The title "Roof of the World" is a testament to the unparalleled altitude and significance of regions like the Tibetan Plateau, Shandur Pass, and the Pamir Mountains. Each of these areas contributes uniquely to global geography, culture, and ecology.
The Tibetan Plateau stands out as the most recognized "Roof of the World", influencing global climate and serving as a cultural and spiritual hub. Meanwhile, Pakistan’s Shandur Pass and the Pamir Mountains offer their distinct charm, blending natural beauty with cultural richness.
These regions are not just geographical wonders but also symbols of human resilience and the beauty of nature. Exploring these "Roofs of the World" promises a journey filled with awe, inspiration, and discovery.
Why is the Tibetan Plateau Called the “Roof of the World”?
The Tibetan Plateau is called the "Roof of the World" due to its unmatched altitude and its role as a climatic and geographical giant. It influences weather patterns across Asia, acting as a natural barrier to monsoons and a source of many of the world’s largest rivers, including the Yangtze, Mekong, and Indus. Its strategic location and ecological significance make it a cornerstone of global environmental systems.
Shandur Pass: Pakistan’s “Roof of the World”
In Pakistan, the Shandur Pass is often referred to as the "Roof of the World". Located in the Gilgit-Baltistan region, it connects the Chitral and Gilgit valleys. At an altitude of 3,700 meters (12,139 feet), the Shandur Pass is renowned for its Shandur Polo Festival, which is held annually and attracts tourists from around the world.
Unique Features of Shandur Pass
-
High-Altitude Polo Ground
Shandur hosts the world’s highest polo ground, where local teams from Chitral and Gilgit compete in a historic match during the Shandur Polo Festival.
-
Spectacular Landscapes
The pass offers stunning views of snow-capped peaks, lush green valleys, and serene lakes, making it a paradise for nature lovers.
-
Cultural and Historical Importance
Shandur has been a cultural meeting point for centuries, fostering connections between the people of Chitral and Gilgit.
Why is Shandur Pass Known as the “Roof of the World”?
Shandur Pass earns its title due to its high altitude and the cultural significance of its polo ground. The pass symbolizes resilience and tradition, with its annual festival serving as a celebration of local culture and sportsmanship. For adventurers and tourists, it offers an unforgettable experience of Pakistan’s natural beauty.
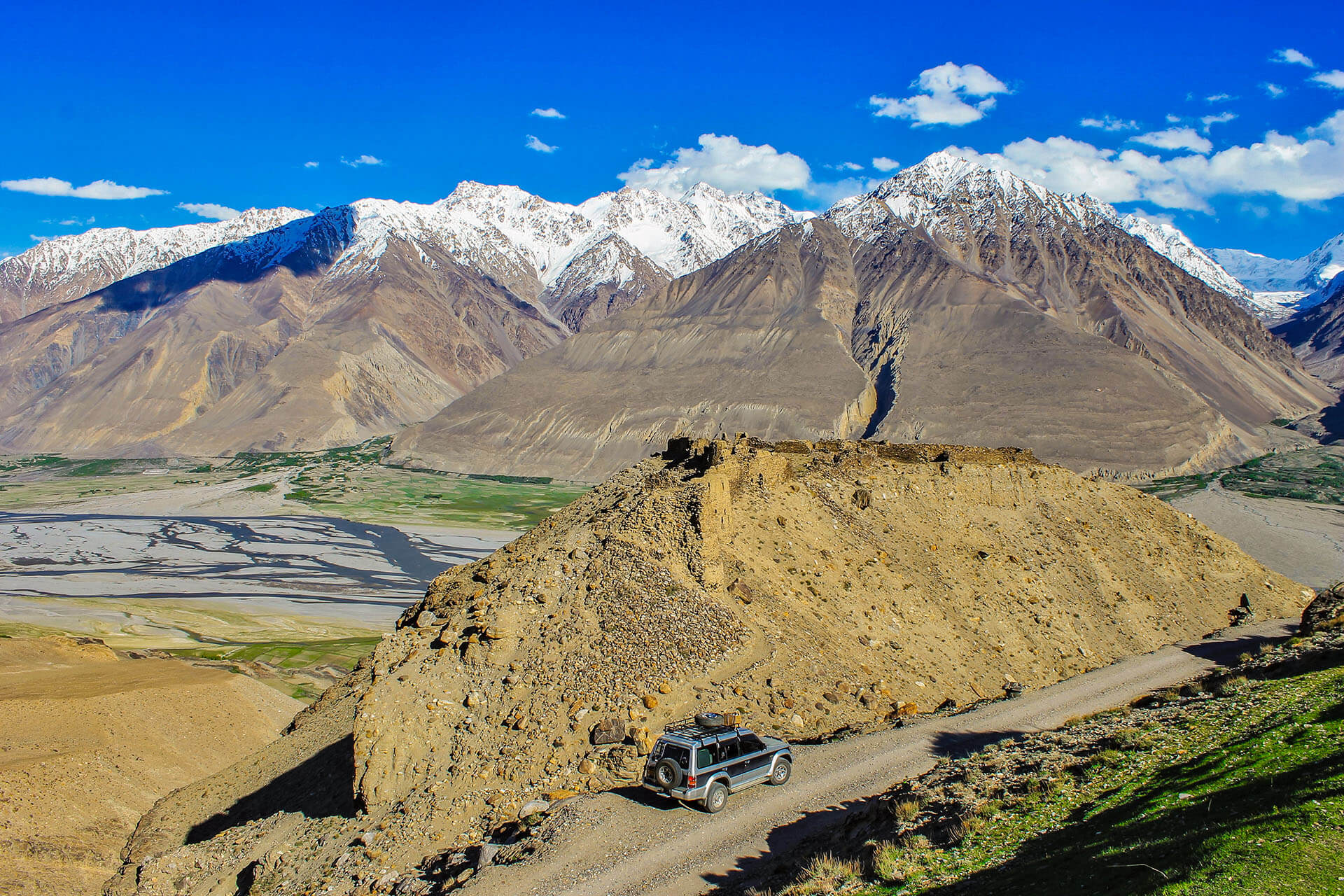
The Pamir Mountains: Another “Roof of the World”
The Pamir Mountains, often referred to as the "Roof of the World", are located in Central Asia, primarily in Tajikistan, with extensions into Afghanistan, China, and Kyrgyzstan. This mountain range forms a natural intersection of the Himalayas, Karakoram, Hindu Kush, and Tien Shan ranges.
Highlights of the Pamir Mountains
-
Geographical Importance
-
The Pamirs serve as a strategic link between Asia and Europe, historically part of the ancient Silk Road.
-
They are home to some of the world’s tallest peaks, including Peak Ismoil Somoni.
-
-
Ecological Diversity
-
The region is rich in biodiversity, with species adapted to its harsh climate.
-
Glaciers in the Pamirs are crucial for the water supply in Central Asia.
-
-
Cultural and Historical Legacy
-
The Pamirs have been a melting pot of cultures and traditions, with influences from Persian, Chinese, and Russian civilizations.
-
Why Are the Pamirs Called the “Roof of the World”?
The Pamir Mountains’ high altitude, coupled with their historical significance as a crossroads of civilizations, earns them the title "Roof of the World". Their challenging terrain and breathtaking beauty continue to captivate explorers and adventurers.
Comparing the “Roofs of the World”
|
Region |
Location |
Average Elevation |
Key Features |
|
Tibetan Plateau |
China, India, Nepal |
4,500 meters |
Largest and highest plateau globally |
|
Shandur Pass |
Pakistan |
3,700 meters |
World’s highest polo ground |
|
Pamir Mountains |
Tajikistan, Central Asia |
4,000 meters |
Intersection of major mountain ranges |
Importance of These Regions
1. Environmental Significance
-
These regions are critical for regulating global climate and water systems.
-
They act as sources for major rivers, sustaining billions of people.
2. Cultural and Historical Value
-
The Tibetan Plateau is central to Tibetan Buddhism and Asian spirituality.
-
Shandur Pass and the Pamirs have rich histories tied to trade routes and cultural exchanges.
3. Tourism and Adventure
-
These areas attract tourists, adventurers, and researchers seeking unique landscapes and experiences.
-
Activities like trekking, mountaineering, and cultural festivals are major draws.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which valley is known as the “Roof of the World”?
The Tibetan Plateau is widely recognized as the "Roof of the World". However, the term is also used for regions like the Shandur Pass in Pakistan and the Pamir Mountains in Central Asia.
2. Why is the Tibetan Plateau called the “Roof of the World”?
The Tibetan Plateau is called the "Roof of the World" due to its extreme elevation, vast size, and geographical significance.
3. What makes Shandur Pass unique?
The Shandur Pass is home to the world’s highest polo ground and hosts the annual Shandur Polo Festival, a cultural and sporting event.
4. Where are the Pamir Mountains located?
The Pamir Mountains are located in Central Asia, spanning countries like Tajikistan, Afghanistan, and China.
5. How do these regions impact the environment?
These regions influence global weather patterns, act as vital water sources, and host unique ecosystems critical for biodiversity.




.gif)















Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com