Lignite coal, often referred to as "brown coal," is one of the most abundant forms of coal found around the world. It plays a crucial role in the global energy market due to its high availability and relatively low cost. In this article, we will explore the largest lignite coal reserves in the world, with a particular focus on the Thar Coalfield in Pakistan, which is one of the largest lignite coal reserves globally.
What is Lignite Coal?
Lignite coal is a type of coal that is considered to be in the early stages of coalification. It is brownish-black in color and has a relatively low energy content compared to other types of coal like bituminous coal or anthracite. Lignite is often used in power generation, particularly in areas where it is abundant and easily accessible. It is typically found in shallow deposits, which makes it easier and cheaper to mine.
Lignite Coal vs Other Coal Types
-
Lignite: The lowest rank of coal, with a high moisture content and low energy output.
-
Sub-bituminous Coal: A higher rank than lignite, with more energy content.
-
Bituminous Coal: A medium-rank coal with a higher energy content, commonly used in electricity generation.
-
Anthracite: The highest rank of coal, with the highest energy content and the lowest moisture content.
The discovery of the Thar Coalfield in 1991 has placed Pakistan among the top 20 countries with the largest coal reserves in the world. The Thar Coalfield is a valuable resource for Pakistan’s energy sector, and its potential for power generation is immense. While there are environmental concerns associated with the use of lignite coal, efforts are being made to adopt clean coal technologies and sustainable practices to minimize the impact.
The development of the Thar Coalfield is a crucial step towards achieving energy security for Pakistan and reducing its reliance on imported energy sources. With continued investment and innovation, the Thar Coalfield can play a key role in powering Pakistan’s future and driving economic growth.
Where Are the Largest Lignite Coal Reserves Located?
Lignite coal reserves are spread across various parts of the world. Some of the countries with the largest lignite coal reserves include:
-
Germany: Germany is home to some of the largest lignite coal reserves globally, with extensive deposits found in regions like the Rhineland area.
-
United States: The U.S. has significant lignite reserves, particularly in states like Texas, North Dakota, and Montana.
-
Russia: Russia has large lignite coal reserves, mainly located in Siberia.
-
China: China is another country with vast lignite coal reserves, especially in the northern and western parts of the country.
-
India: India is one of the top producers of lignite coal, with major reserves in states like Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan.
However, one of the most significant discoveries of lignite coal in recent years has been the Thar Coalfield in Pakistan.
The Thar Coalfield: Pakistan's Largest Lignite Coal Reserve
Discovery of the Thar Coalfield
The Thar Coalfield is located in the Tharparkar District of Sindh Province in Pakistan. It is one of the largest lignite coal reserves in the world. The Thar Coalfield was discovered in 1991 by the Geological Survey of Pakistan (GSP) and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). This discovery placed Pakistan among the top 20 countries with the largest coal reserves globally.
Size and Significance of the Thar Coalfield
The Thar Coalfield is the 16th largest coal reserve in the world, with an estimated 175 billion tons of lignite coal. This massive reserve holds the potential to transform Pakistan's energy sector, as it can provide a long-term source of fuel for power generation. The discovery of the Thar Coalfield has been a game-changer for Pakistan, as it holds the key to reducing the country’s dependence on imported energy sources.
The Role of Thar Coalfield in Pakistan’s Energy Future
One of the primary uses of lignite coal from the Thar Coalfield is power generation. The government of Pakistan, in collaboration with private investors and international partners, has initiated several projects to harness the energy potential of the Thar Coalfield. These projects aim to convert lignite coal into electricity, which will be used to meet the growing energy demands of the country.
Thar Coalfield Power Projects
-
Thar Coal Block-II Power Plant: This project, developed by Engro Powergen and other partners, is one of the first major power plants in the Thar region. It aims to produce 660 MW of electricity using Thar coal.
-
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) Projects: Under the CPEC initiative, several power plants are being developed in the Thar region. These plants will utilize lignite coal from the Thar Coalfield to generate electricity for Pakistan’s national grid.
-
Thar Coal Mining Projects: Along with power plants, mining projects are also underway to extract lignite coal from the Thar Coalfield. These projects aim to increase the supply of coal for domestic use and export.
Impact on Pakistan’s Energy Security
The development of the Thar Coalfield is a crucial step towards achieving energy security for Pakistan. By tapping into the vast lignite coal reserves of Thar, Pakistan can reduce its reliance on imported oil and gas, which are costly and subject to price fluctuations. The use of local lignite coal for power generation will help stabilize the country’s energy supply and reduce the burden of energy imports.
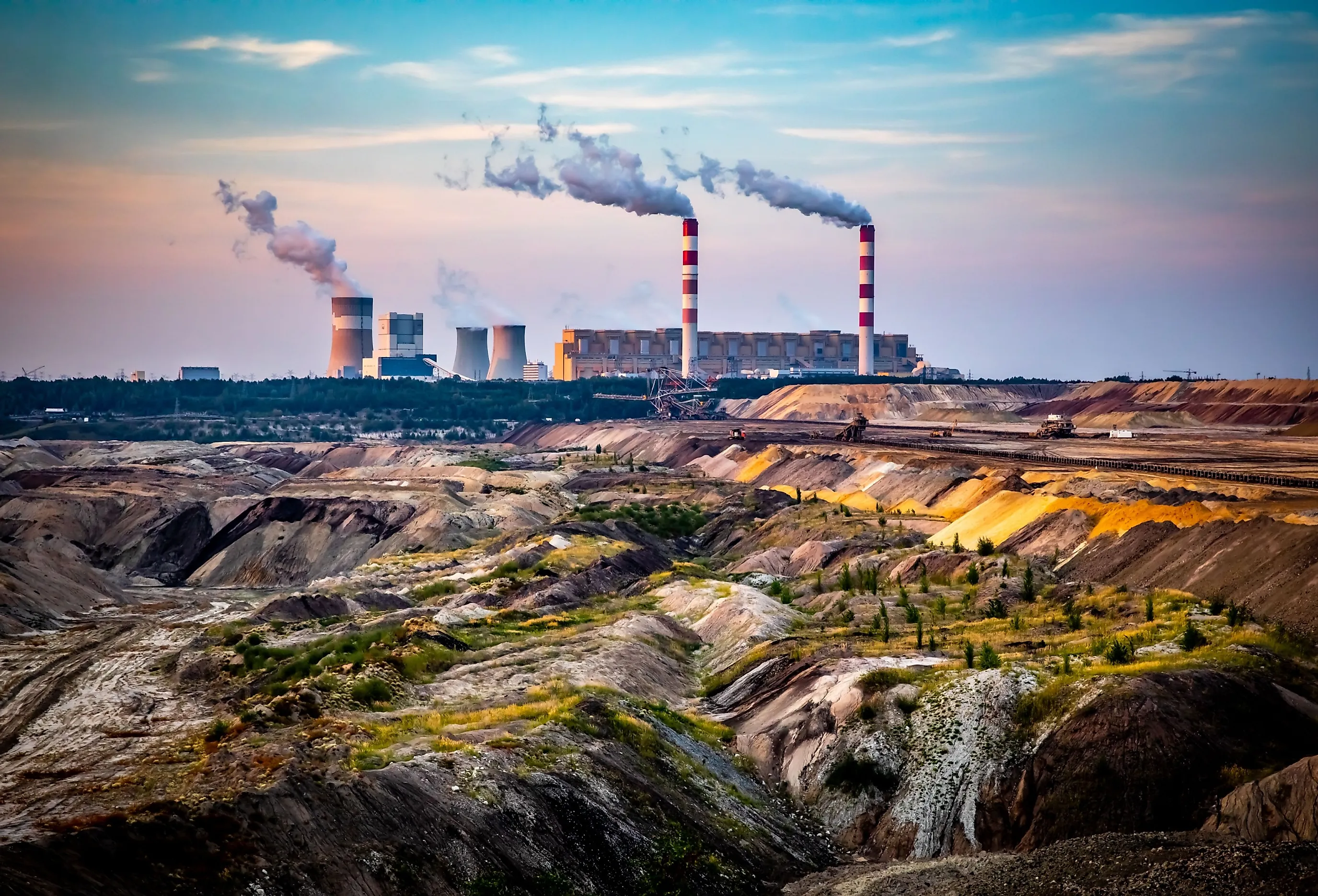
Environmental Considerations of Lignite Coal
While lignite coal is an important energy resource, its use has environmental implications. The burning of lignite coal produces greenhouse gases and other pollutants that contribute to air pollution and climate change. Additionally, mining operations in the Thar Coalfield could lead to land degradation, water scarcity, and other environmental challenges.
Efforts to Minimize Environmental Impact
To mitigate the environmental impact of lignite coal mining and power generation, several measures are being taken:
-
Clean Coal Technology: Efforts are being made to adopt clean coal technologies that can reduce emissions from coal-fired power plants.
-
Environmental Regulations: The government of Pakistan has implemented environmental regulations to ensure that mining and power generation projects in the Thar region are carried out in an environmentally responsible manner.
-
Sustainable Mining Practices: Sustainable mining practices are being promoted to minimize land degradation and ensure the long-term viability of the Thar Coalfield.

FAQs About the Thar Coalfield and Lignite Coal
1. Where is the Thar Coalfield located?
The Thar Coalfield is located in the Tharparkar District of Sindh Province in Pakistan.
2. When was the Thar Coalfield discovered?
The Thar Coalfield was discovered in 1991 by the Geological Survey of Pakistan (GSP) and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
3. How large is the Thar Coalfield?
The Thar Coalfield is one of the largest lignite coal reserves in the world, with an estimated 175 billion tons of coal.
4. What is the significance of the Thar Coalfield for Pakistan?
The Thar Coalfield holds the potential to transform Pakistan’s energy sector by providing a local source of fuel for power generation, reducing the country’s dependence on imported energy.
5. What projects are being developed in the Thar Coalfield?
Several power generation and mining projects are being developed in the Thar Coalfield, including the Thar Coal Block-II Power Plant and various CPEC-related projects.
6. What are the environmental concerns related to lignite coal?
The burning of lignite coal produces greenhouse gases and pollutants, while mining operations can lead to land degradation and water scarcity.





.gif)








.gif)







Sign in
to continue to ilmkidunya.com