The solar energy industry is witnessing a revolutionary shift with the introduction of perovskite solar panels. Japanese scientists have developed these next-generation solar panels that boast an efficiency of 40%, significantly surpassing traditional silicon-based panels. With lower costs, higher efficiency, and greater flexibility, perovskite solar technology is set to redefine renewable energy adoption worldwide.
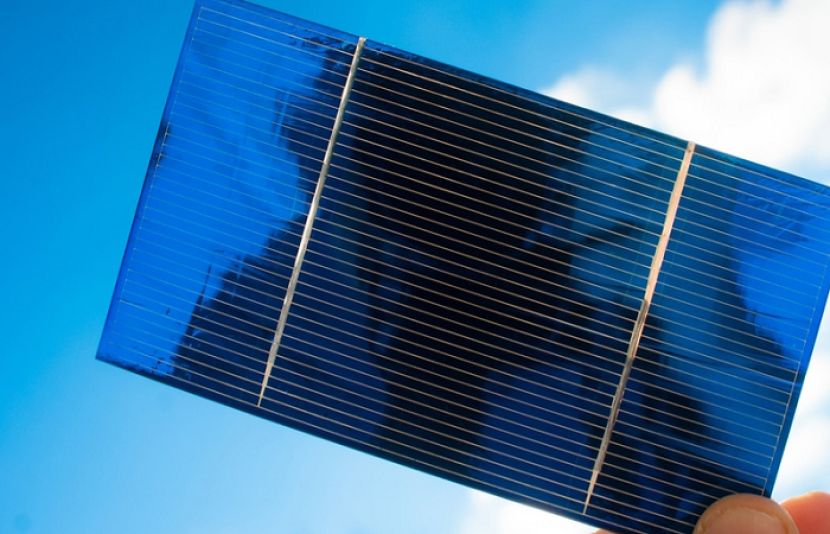

Traditional Silicon vs. Perovskite Solar Panels
Efficiency Comparison
Traditional crystalline silicon solar panels have an efficiency ranging from 15% to 30%, whereas perovskite solar panels can achieve up to 40% efficiency.
| Feature | Silicon Solar Panels | Perovskite Solar Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 15% - 30% | Up to 40% |
| Manufacturing Cost | High | Low |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible |
| Performance in Low Light | Low | High |
| Installation Areas | Limited to roofs | Walls, vehicles, flexible surfaces |
Why Perovskite Solar Panels Are Game Changers
1. Higher Efficiency
-
The 40% efficiency rate is almost double that of conventional solar panels, leading to higher energy output.
2. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
-
Perovskite materials are cheaper and easier to produce compared to silicon.
-
The production process is simpler and faster, reducing costs further.
3. Works in Low Light & Harsh Weather
-
Unlike silicon panels, perovskite solar cells perform exceptionally well in cloudy, rainy, and low-light conditions.
-
This ensures consistent energy generation, even in regions with limited sunlight.
4. Greater Flexibility
-
These solar panels are lightweight and bendable, allowing installation on:
-
Walls of buildings
-
Vehicles
-
Glass windows
-
Other unconventional surfaces
-
5. Wide-Scale Implementation by Japan & China
-
The Japanese government plans to install these panels on government buildings, rooftops, and vehicles to generate 20,000 MW of solar power over the next five years.
-
China is rapidly advancing in perovskite solar panel production due to abundant tin and lead resources, making it a future global leader in this technology.
-
Chinese companies are already producing hybrid silicon-perovskite solar panels with 39% efficiency.
Impact on the Renewable Energy Market
1. Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels
-
The higher efficiency and lower cost of perovskite panels will accelerate the transition from fossil fuels to solar energy.
2. Increased Adoption in Urban Areas
-
The ability to install these panels on walls and vehicles makes them ideal for urban energy solutions, reducing the space constraints of traditional solar panels.
3. Boost to Green Energy Investments
-
As governments and corporations recognize the potential of perovskite solar technology, more investment and research funding will flow into the renewable energy sector.
Challenges & Future Outlook
Challenges
-
Durability Issues: Perovskite materials are less stable than silicon, requiring further research to enhance longevity.
-
Scalability: Mass production at a commercial scale needs optimization for cost and efficiency.
-
Environmental Concerns: Some perovskite materials contain lead, requiring eco-friendly alternatives to ensure sustainability.
Future Developments
-
Research is underway to enhance the stability and lifespan of perovskite panels.
-
Scientists are exploring lead-free perovskite materials for more eco-friendly solutions.
-
Hybrid perovskite-silicon panels could soon become the standard, combining the best of both technologies.
Related Articles
-
Ilmkidunya 26/Jun/2025
How to Prepare for Competitive Exams Effectively
-
Ilmkidunya 10/Jun/2025
From Curiosity to Career A Purpose-Driven Journey Through the 4D Growth Framework
-
Ilmkidunya 10/Jun/2025
The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence in Everyday Life
-
Ilmkidunya 30/May/2025
Over 1 Billion Users: Meta AI Sets New Standard in AI Technology
-
ilmkidunya 27/May/2025
AI in Education – Will Students Stop Doing Homework in the Future?
-
ilmkidunya 27/May/2025
Tech Skills That Will Never Go Out of Demand
-
Ilmkidunya 12/May/2025
Mind Mapping for Smarter Studying: A Visual Learning Guide
-
Ilmkidunya 09/May/2025
How Computers Might Solve Problems We Don’t Even Understand Yet
-
Ilmkidunya 08/May/2025
Solving Compatibility Issues in Cross-Platform App Development
-
Ilmkidunya 08/May/2025
How Agile Methodologies Solve Project Management Problems

.gif)









.png)